What is Search Intent and Why Does it Matter in SEO?
I'm sure you've heard about "Search Intent" or "User Intent" a bunch of times, but you may not have given it the importance it has when it comes to ranking higher on SERPs. As it turns out, Search Intent is crucial, so much so that it's currently Google's number one goal when it comes to meeting user expectations. So, let's dig into it!
Inside this article
-
Search Intent explained
-
What types of Search Intent are there?
-
Informational
-
Navigational
-
Commercial
-
Transactional
-
A practical way to understand Search Intent by analyzing SERPs
-
Best Search Intent practices to rank higher
-
Final Note
Search Intent explained
Simply put, search Intent is the intention behind a user's query: what they expect to get as a result of a particular search. Of course, we can't get inside other people's minds, but we're all human, and when it comes to Search Intent, our patterns are very similar. This being said, the easiest way to understand the concept is by taking your own Google searches as an example.
If I think of my latest queries, they go all the way from "best fall destinations Europe" to "sushi near me" to "Wix login."
And these actually make great examples to understand the whole concept. I'll explain why:
What would you think I want to get if I search for "best summer destinations in Europe"? Probably lists and rankings of the best summer spots, travel blogs with pictures comparing destinations, and so on. And you'd be right!
A user making this kind of query is evaluating the idea of traveling but hasn't yet decided where. If I got a bunch of airline sites and ticket fares instead of articles and travel blogs, I'd be pretty disappointed. And the last thing Google wants is for me (or anyone) to be disappointed.
Try opening a search tab and typing "best summer destinations in Europe" to see what you get…

Ta-dah! Rankings and travel blogs! That's Google satisfying Search Intent successfully.
Now let's go on to my second query: "sushi near me." Of course, this means I want to eat sushi around my area, so I'd expect results such as nearby restaurants or maybe even delivery options. It would be frustrating to get SERPs with sushi recipes or informative articles on where and how they invented sushi. I want to EAT sushi, not learn the history behind it.
Let's test-drive this query on Google too.
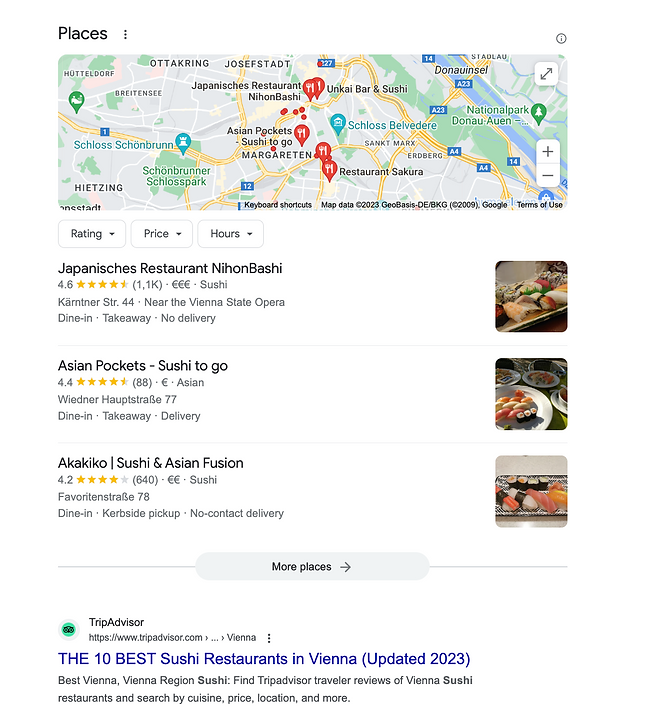
Success! Google knows I'm craving some sushi and tells me where to get it. (You also probably correctly guessed that I'm currently in Vienna).
Now to my last query example: "Wix login." My intent here is crystal clear: I'm too lazy to type the Wix URL, so I type in "Wix login" on the search bar and expect Google to do its job, which it brilliantly does:

Ok, now we know what Search Intent is and why it's crucial for search engines to satisfy it. Let's make it even more precise and organized by reviewing the kinds of existing searches.
What types of Search Intent are there?
Fortunately, there's not an infinite number of Search Intent categories out there. Instead, more than 99% of all searches fall into one of these 4:
-
Informational:
As the name states, the user is looking for information. These searches are sometimes formulated as questions such as:
"Who won best picture at the Oscars 2022?"
"How do vaccines work?"
But not necessarily. For example:
"Rules of chess"
"US Open schedule today"
"Aretha Franklin"
"change flat tire"
those are also informational queries!
In this case, the searcher wants to learn more about a particular topic or person, so the desired SERPs should include articles, biographies, tutorials, Wikipedia articles, etc.
2. Navigational:
This is probably the most straightforward Search Intent type. Like the Wix example, in this case, the user already knows where they want to go and types it on the search bar:
"Wordpress login"
"Facebook"
"Pinterest"
"ESPN"
As expected, Google will know you want access to a particular site and rank it first.
3. Commercial:
Suppose you're familiar with the marketing funnel. In that case, a commercial search is still within the "interest" and "desire" parts of the funnel, meaning the user is keen on making a purchase but isn't quite ready to take action. This kind of query is about research, brand comparisons, prices, reviews, and all the information a user might find helpful to make a good purchase. For example:
"Nike vs. Adidas running shoes"
"Best mirrorless cameras 2023"
“Top boutique hotels in Tulum”
"Fuji XT5 review"
We'll most probably get specialized blogs, rankings, listIcles, and expert reviews on SERPs for this type of Search Intent.
4. Transactional
This Search Intent would be at the bottom end of the marketing funnel, the "action" part where the user is card-in-hand, ready to purchase. Some examples would look like this:
"Buy AirPods pro"
"Nike Lebron on sale"
"Cheap flights to Thailand"
"Lollapalooza tickets"
Undoubtedly, the SERPs will show you product pages and Google shopping ads to get those AirPods ASAP (or whatever else you want).
A practical way to understand Search Intent by analyzing SERPs
Now that we've soaked in the definition of Search Intent and its types, it's time for a fun little exercise that will make you go, "AHHHH! I get it!"
First, a quick recap on a SERP: It's a Search Engine Result Page. In other words, SERPs are the pages that appear when you search for something on Google and display several helpful sites for your particular query.
Now to the practical task. Let's look these up on Google, and before you hit "enter," try and guess what kind of results you'll get:
-
Buy puma CALI
-
Best beaches in Croatia
-
How to make bread at home
-
Nikon or Canon mirrorless
You probably guessed correctly, and then Google confirmed your hypothesis, right?
-
"Buy puma CALI" has a Transactional Search Intent which is why your SERPs will show e-commerce sites and, most likely, stores in your area where you can get those shoes.
-
"Best beaches in Croatia" has a Commercial Search intent, and you most definitely got a lot of travel blog posts.
-
"How to make bread at home" has an Informational Search Intent. Clearly, you want to make bread at home, so you'll get dozens of recipes. Getting video results is also pretty common with "How to" or tutorial-type searches. The same will probably happen if you type "How to play backgammon" or "Yoga tutorial for beginners."
-
"Nikon or Canon mirrorless" is also a Commercial kind of search because you intend to compare the two brands, so I'm sure you got a lot of expert reviews, comparative tables, pics, and video reviews.
To prove just how good Google is at deciphering Search Intent, slightly adjust the last query and type "Buy Canon mirrorless." What happens? The Search Intent changes entirely to a Transactional one. Google knows you're no longer comparing but looking to buy and shows you pages where you can purchase a camera.
Best Search Intent practices to rank higher
Now to the most crucial bit. I'm sure you've understood what Search Intent is, but now you're wondering how to put this knowledge to good use when it comes to ranking your page higher.
We all agree that goal of any SEO-optimized page is to rank in the top 5, or at least the top 10 on SERPs, because, let's face it, very few people browse past page 2.
So, what can you do to optimize your page? Here are 3 good practices to rank higher using Search Intent:
1. Always check what the current top-ranking pages are showing for your targeted keywords
Google has become super clever at figuring out Search Intent, which means if it ranks certain pages on top, those are the ones with the content users expect to find.
So, if your targeted keyword is "Yoga poses," and you're mostly getting images and video tutorials, that's what you should aim at.
An easy way of checking this is by analyzing the content type of high-ranking pages on SERPS. Are they articles? Lists? Blog posts? Product pages? Check for any given query, and you'll find a dominant content type, then make sure your content aligns with it. In this case, being original and trying to go a different way is not the smartest move.
2. Check out user-related searches
You may have noticed that when you make a query, there's a section at the bottom where Google lists related searches. Other people are using these searches to find similar results with keywords or phrasings you might not have considered.
For example, for the query "making pizza" we get the following related searches:

This is an excellent indicator of what the Search Intent is. We see searches with the words "how to," "step-by-step," and "pizza dough," so it's evident that users are looking to make pizza at home.
If you sell pizza, even if it has a homemade taste, "making pizza" wouldn't be a great keyword to consider because people are not looking to buy a product; they want to MAKE it. However, if you're smart enough, you might consider a blog where you teach people how to make their own pizza and then sell them ready-made dough, for example.
3. Optimize your content to fit your Search Intent
Even if you pick great keywords and create the content type that suits your Search Intent, there's always room for improvement on your page. How? By giving the user more of what they need and less of what they dislike. I assure you that this won't go unnoticed by Google.
If you see that specific keywords get SERPs with many images and videos, don't hesitate to include those. Rich media can make all the difference, especially in tutorials, reviews, step-by-step guides, and "how to" queries. If your audiovisual content is original, unique, and custom-made for your page, you'll stand out even more.
Look for high-ranking pages' strong and weak aspects and profit from them. For example, maybe page nº1 has impressive visuals, but the information is not concise or well organized. Perhaps nº2 displays clear and organized content but lacks an explanatory video or uses too small a font. Take the best of what all top-ranked pages are doing and avoid their mistakes to get to that sweet spot where you deliver just what users want.
Final Note
We've seen how vital Search Intent is for SEO and SERP rankings. Remember: no matter how high the search volume is for a particular keyword, if it doesn't match Search Intent, it won't be relevant for the user; therefore, Google will push you down the rankings. So when doing keyword research, always remember to consider Search Intent.
